Anyone who grew up on the south side of Chicago or the south suburbs or in northwest Indiana will likely be familiar with the Elgin, Joliet and Eastern Railway. But others are less likely to be familiar with this smaller railroad.
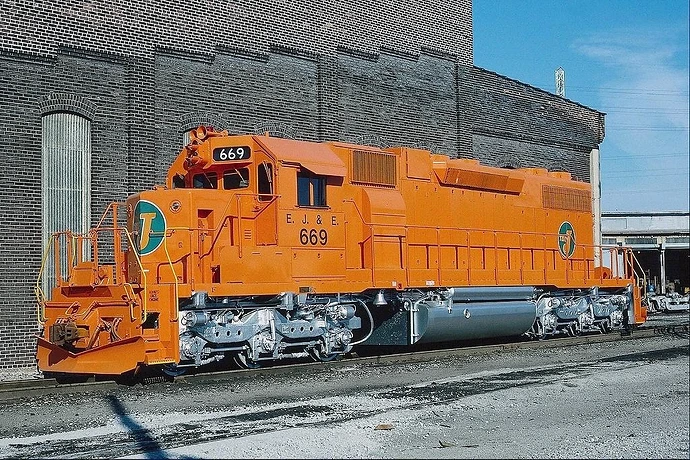
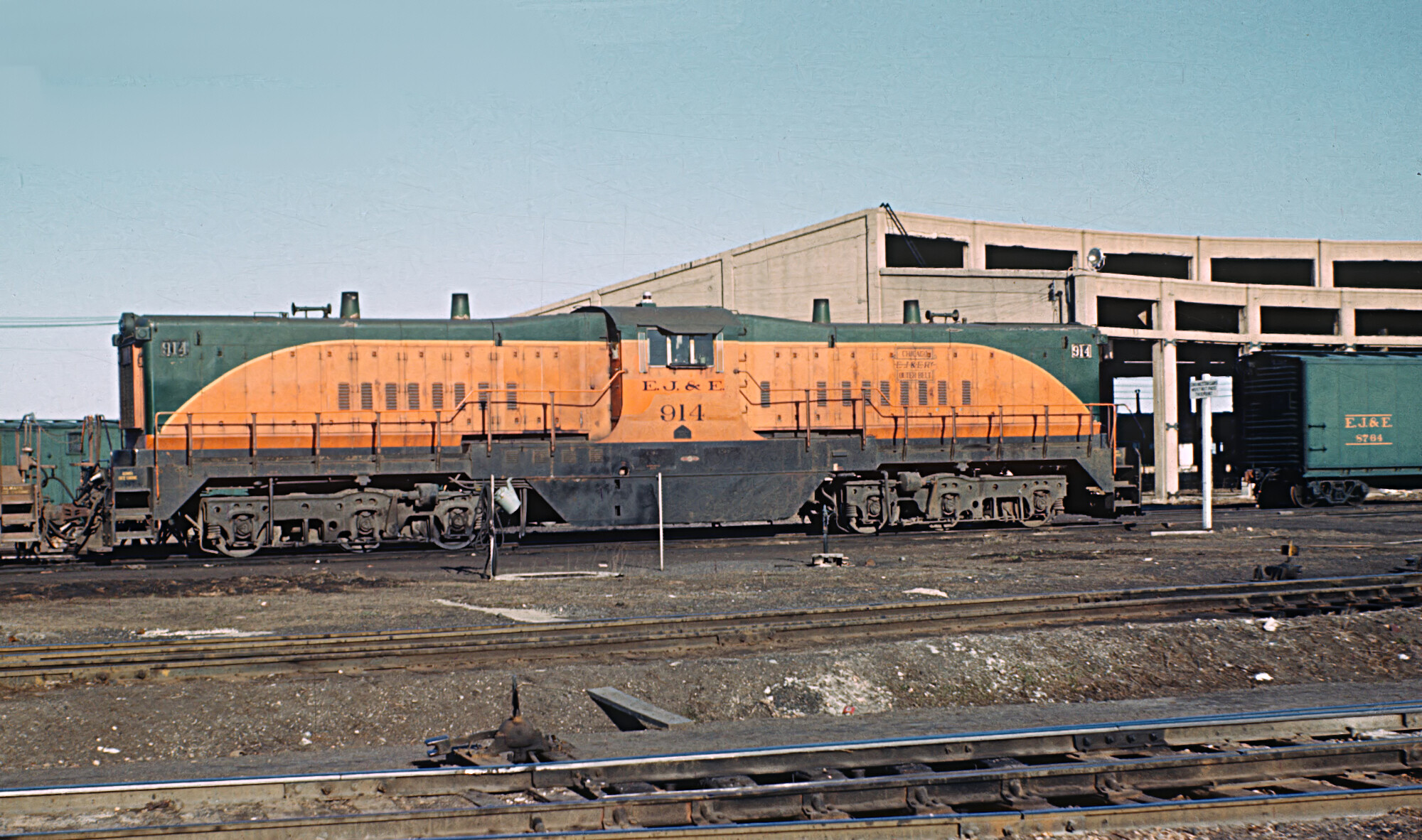
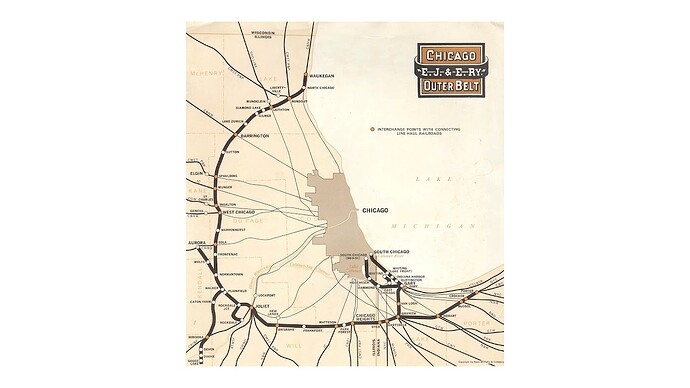
The Elgin, Joliet and Eastern Railway, affectionately know as "The EJ&E, was a Class II railroad that made a circular path between Gary, Indiana and Waukegan, Illinois. The railroad served as a link between Class I railroads traveling to and from Chicago, although it operated almost entirely within the city’s suburbs, only entering Chicago where it served the U.S. Steel South Works on the shores of Lake Michigan.
Source:https://industrialscenery.blogspot.com/
The Elgin, Joliet and Eastern was created when several local railroads in Illinois and Indiana merged throughout the end of the 19th century. Those railroads included the Joliet, Aurora & Northern Railway and the Elgin, Joliet & Eastern Railway Company of Illinois. The Elgin, Joliet and Eastern Railway began operations on December 4, 1888, through the merger of these two systems. After its creation, the railroad expanded by purchasing several other smaller lines including the Waukegan & Southwestern Railway; Gardner, Coal City & Northern Railway; Western Indiana Railroad; and the Chicago, Lake Shore & Eastern Railway.
The EJ&E began to serve industries in the Hammond-East Chicago-Whiting industrial district by acquiring trackage rights in 1894. However, construction of the present line to Gary, Whiting and South Chicago was initiated in 1899 by the Griffith and Northern Railway. Connections with the Chicago, Lake Shore and Eastern Railway and the Western Indiana Railway further penetrated the district, although the EJ&E subsequently acquired both lines. In 1898 the EJ&E merged with four other non-railway companies to form Federal Steel Company. In 1901, United States Steel Corporation was formed from a merger that included Federal Steel, and U.S. Steel thereby acquired the railroad.
Unlike the Belt Railway of Chicago and Indiana Harbor Belt which were just that, belts, the EJ&E was not even a belt road. While a branch did reach South Chicago, EJ&E’s main line was situated far away from downtown Chicago and handled as much through traffic as it did terminal/interchange business.
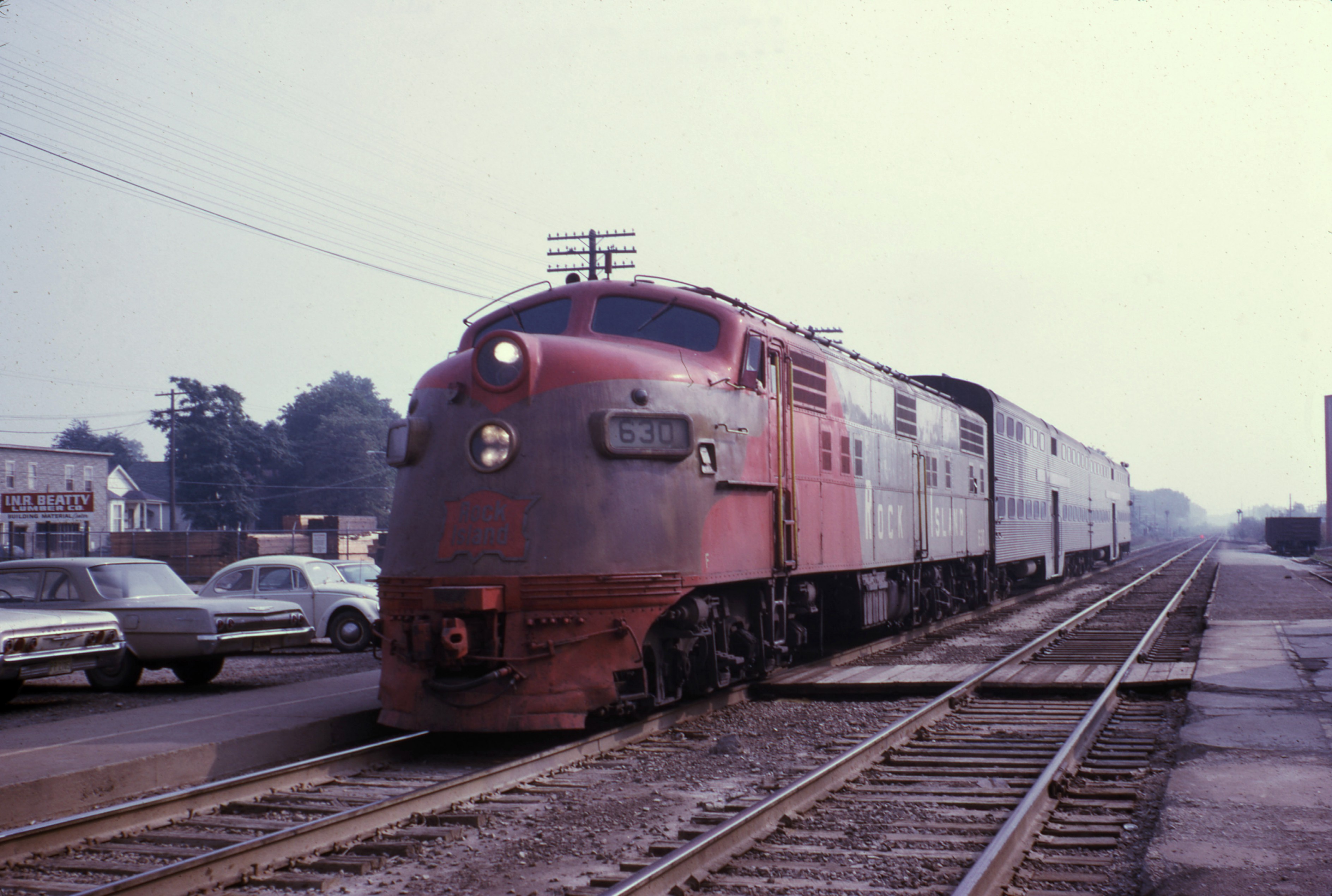
The EJ&E abandoned passenger trains early on, shifting focus exclusively to freight. The railroad’s passenger services began with the start of operations in January 1889. The railroad stopped operating passenger trains in 1907, but continued passenger service until 1909. During those two years, passengers would be transported by caboose.
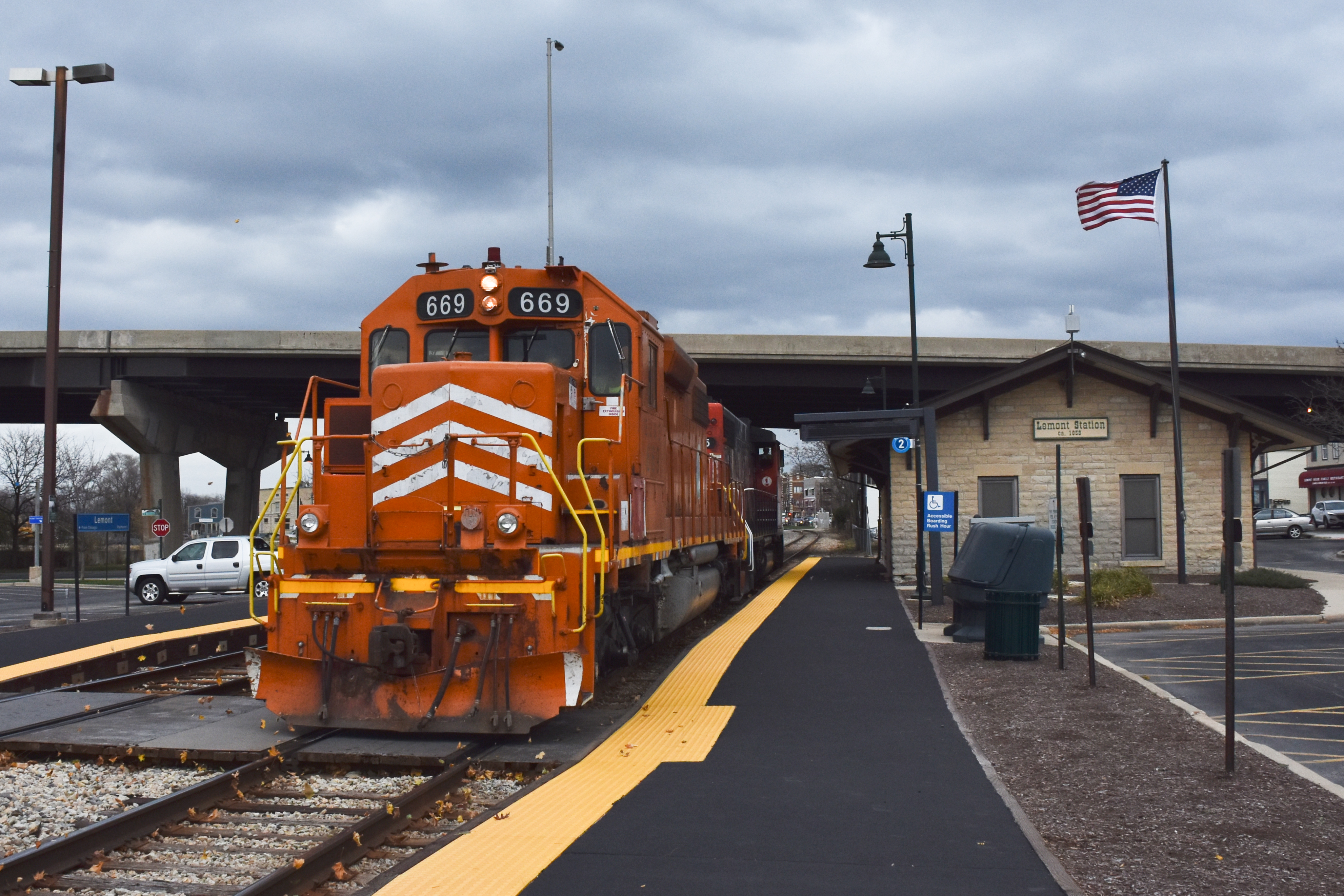
On September 26, 2007, the Canadian National Railway announced that it planned to purchase a majority of the EJ&E, leaving a portion of the line in Indiana to be reorganized as the Gary Railway. The purchase was approved on December 24, 2008, by the U.S. Surface Transportation Board, and the deal was consummated effective February 1, 2009. On December 31, 2012, Canadian National announced that the merger of the EJ&E into Wisconsin Central Ltd. On January 1, 2013, the EJ&E effectively ceased to exist, 124 years to the day it was founded.
Rich